The photovoltaic industry is booming!
stated our interim CFO at a rapidly growing PV system manufacturer.
A look at current trends and developments
HANSE Interim Team Research: The photovoltaic sector is currently experiencing a real boom. More and more companies and private households in Germany are turning to solar power to hedge against fluctuating energy prices and contribute to climate protection. What developments can be expected in the coming years and what opportunities and challenges are emerging for the industry?
What is photovoltaics?
Photovoltaics, derived from the Greek words for light “photo” and electrical voltage “volt”, refers to the conversion of sunlight into electrical energy. This is done with the help of solar modules, which consist of numerous solar cells and can be installed on roofs, facades or as free-standing solar fields. The electricity generated is either used directly, stored or fed into the public grid.

Photovoltaics is not only a cheaper alternative for generating electricity, it is also a clean, renewable energy source that reduces CO2 emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
Photovoltaics is one of the most important technologies in the field of renewable energies and is one of the most important energy technologies in the world.
In Germany, photovoltaics plays a central role in the energy transition.
Current market overview of photovoltaics
Photovoltaic technology has come a long way since its introduction in the 1950s. The industry experienced its first strong growth from 2004, which was curbed in 2012 by political decisions such as the so-called “solar cap”. This limit on installed capacity led to a decline in expansion. It was not until the solar cap was lifted in 2020 and the political realignment that the industry began to grow strongly again.
Today, photovoltaics is on the rise again in Germany. Despite pandemic-related supply bottlenecks and long waiting times, demand for solar cells has risen continuously in recent years. In 2023, around 3.7 million photovoltaic systems were installed in Germany, generating around 62 terawatt hours of electricity and thus covering around 12% of gross electricity consumption.
The demand for photovoltaic systems continues unabated, which is partly due to increased environmental awareness and persistently high energy prices.
Both private households and companies are increasingly investing in solar systems to secure their energy supply and reduce costs.
While photovoltaic systems still accounted for half of all newly installed energy capacities in 2021, this figure had risen to ⅔ worldwide by 2022.
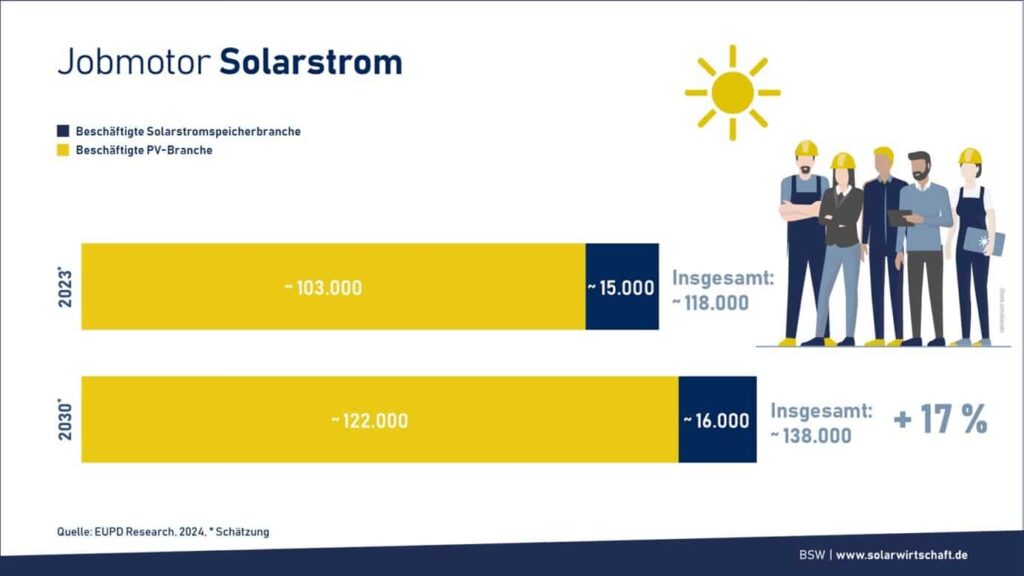
Around 42.3 million tons of CO2-equivalent greenhouse gas emissions could be avoided in 2023 through the use of photovoltaic systems. The industry employed around 103,000 full-time employees and generated a turnover of around 25 billion euros, underlining its central role in the energy transition and the German economy.

Companies and commercial roofs in particular are currently being electrified with the help of photovoltaics. Of those that have not yet installed photovoltaic systems, every second company is currently planning to build a solar power plant on its roof.
Additional growth impetus comes from government subsidy programs and climate protection targets. The Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG) creates the necessary incentive for the use of solar energy through financial incentives and legal framework conditions. In addition, technological advances promote the efficiency of solar modules and reduce production costs.
What are the drivers of photovoltaic growth?
The growth of the photovoltaic sector is being driven by several factors. It is not only increasing environmental awareness that is promoting the expansion of solar energy. Rising energy prices and the desire for independence are also encouraging more and more private individuals and companies to invest in photovoltaics: In particular, current geopolitical crises such as the war in Ukraine or the recent coronavirus pandemic have heightened awareness of the need for a secure and independent energy supply.
In addition, government climate protection targets and subsidy programs are key drivers in the expansion of photovoltaic systems. The Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG), which was first introduced in 2000, sets long-term expansion targets and establishes a legal framework for the promotion of renewable energies. The EEG also creates financial incentives for the use of solar energy: photovoltaic systems that comply with the provisions of the EEG can receive a subsidy.
In addition, the German government’s Solar Package 1, which recently came into force on May 16, 2024, focuses specifically on the promotion of solar energy. It aims to reduce existing bureaucratic hurdles and thus simplify the installation and operation of photovoltaic systems.
At the same time, technological progress with increasing efficiencies and falling production costs for photovoltaic modules are continuing to drive growth. The German Solar Industry Association therefore expects more and more commercial and industrial companies to install solar power systems in order to reduce their energy costs and make them more predictable in the future.
Expectations of market development
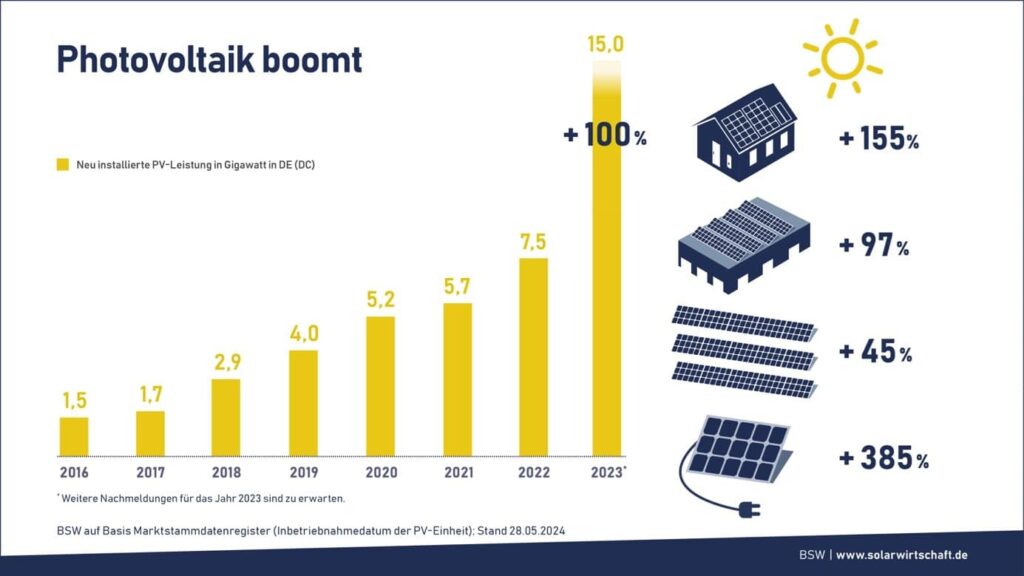
After sales of solar power storage systems and photovoltaic systems doubled last year, newly installed photovoltaic and storage capacities are expected to grow in the lower double-digit percentage range in 2024. This would put the expansion of German solar power systems on the legally defined home stretch of the energy transition: since the most recent amendment on January 1, 2023, the EEG has been pursuing the goal of increasing the share of renewable energies in gross electricity consumption to at least 80% by 2030.
The share of solar power, which covers the electricity demand in Germany, is to be roughly doubled by 2030, from the current 12% to around 25%.
Who will benefit from the boom?
In recent years, the expansion of photovoltaics has led to positive developments in the German economy. This has created numerous new jobs, particularly in and with the solar industry. In addition, the expansion of solar power systems has led to growth in the value chain and an increase in economic output in this sector. The implementation of new technologies and innovations in solar energy has also contributed to the positive development of the German economy.
However, solar power production has not only seen considerable growth in Germany: photovoltaics is also an up-and-coming industry globally. Competition for photovoltaic module manufacturers comes primarily from Asia: in 2023, China was the leader in the production of solar modules and solar cells.
Chinese producers have created considerable production capacity due to the size of the Chinese market and the high demand for solar power in China. This has made it possible to achieve lower unit costs and economies of scale. In addition, considerable progress has been made in Chinese technology development, which has increased product efficiency.
Furthermore, the Chinese government is also supporting the solar market, which has enabled producers to grow rapidly and compete on the global market. As a result, 8 of the 10 largest manufacturers of solar modules today come from China.
Due to increasing competition from abroad, many German manufacturers have had to cease production. Nevertheless, the increased demand within Germany is creating more jobs and is therefore an important job driver in the German energy industry. Ultimately, consumers are the main beneficiaries, as Chinese competition has forced manufacturers around the world to lower their prices for photovoltaics.
Challenges for the further expansion of photovoltaics
Integration into the power grid
- In many places, the sharp rise in solar energy production is reaching the load limits of the existing electricity grid.
- Grid stability is being jeopardized by the high feed-in of solar power.
- Some medium-sized systems cannot be connected to the grid.
- The infrastructure is currently not designed to absorb large amounts of solar energy.
Storage of solar energy
- Need for storage during surplus periods to prevent overloading the electricity grids.
- At present, efficient implementation of storage is not yet possible.
- The focus to date has mainly been on the generation, transportation and consumption of renewable energies.
- The development of necessary storage capacities is lagging behind the rapid expansion of photovoltaic systems.
Staff shortage and lack of skilled workers
- A lack of qualified personnel is hampering the expansion of photovoltaic systems and the necessary reinforcement of the electricity grids.
- Skills shortages and long waiting times are hampering the rapid and sustainable expansion of solar energy.
- In Thuringia, it took an average of 6 months to check the suitability of the local electricity grid for installation in 2023.
- With sufficient personnel, the installation of photovoltaic systems only takes a few days.
Conclusion
Photovoltaics is at the heart of global efforts to achieve a sustainable and climate-friendly energy supply. The impressive progress and dynamic development at both international and national level show that there is a positive trend.
Despite existing challenges, the dynamic development of the sector in Germany and worldwide shows that the future of energy is green. Ongoing political support and technological innovations are strengthening this positive trend, which is likely to continue in the coming years.
What developments do you see in this market in the future?
Feel free to share your experiences and opinions in the comments!
With best regards
Your HANSE Interim Management
Andreas Lau
- https://www.solarwirtschaft.de/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/sharp_reference_rodenaes229.jpg ↩︎
- https://www.solarwirtschaft.de/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/pvvatikan.jpg ↩︎
- https://www.solarwirtschaft.de/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/009_PG_PV_Markt_05_2024_DE.jpg ↩︎
- https://www.solarwirtschaft.de/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/BSW_Grafiken_Jobmotor_DE.jpg ↩︎ ↩︎


